Destructors in Python Explain clearly
 Naveen
Naveen- 0
A destructor is called when an object is deleted or destroyed. The destructor is the reverse of the constructor.
Destructor is used to perform the clean-up activity before destroying the object, such as closing database connections or file handle.
The special method __del__() is used to define a destructor.
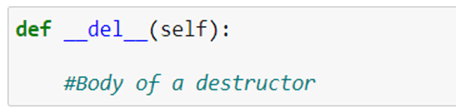
We can define a destructor with any number of arguments.
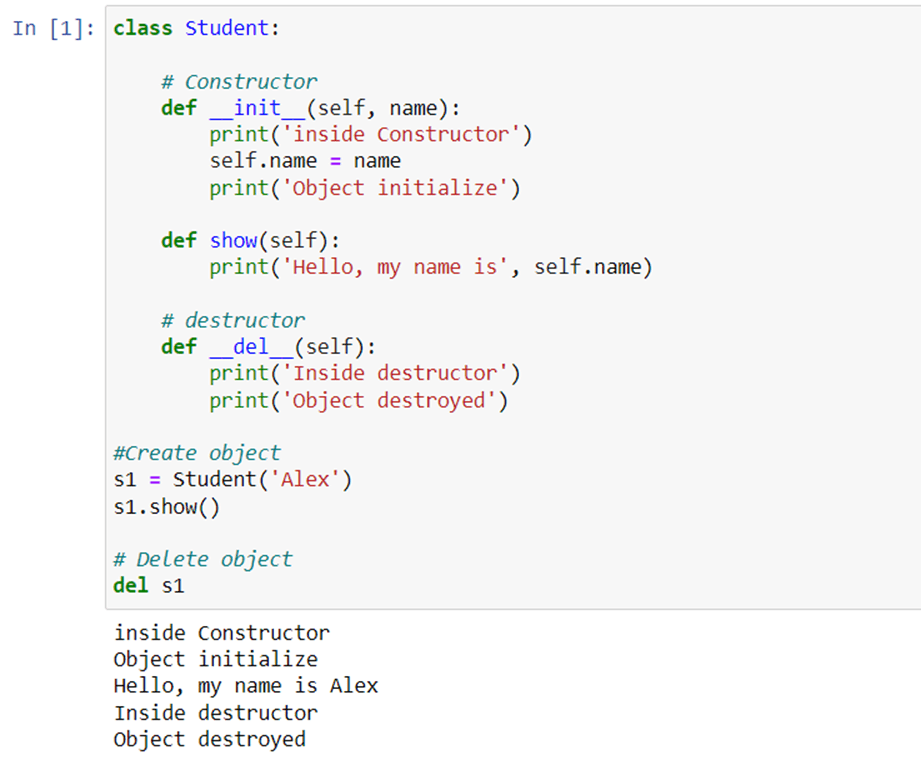
The destructor will not be invoked when we delete object reference.
It will only invoke when all references to the objects get deleted.
The destructor behaves weirdly and doesn’t execute in the following two cases.
- Circular referencing – when two objects refer to each other
- Exception occurred in __init__() method.
Circular referencing
When both objects go out of scope, Python doesn’t know which object to destroy first. So, to avoid any errors, it doesn’t destroy any of them.
Exception in __init__ method
In OOP, if any exception occurs in the constructor while initializing the object, the constructor destroys the object.
Conclusion
In this article, you’ve learned about Destructors in Python and how they can help you delete objects that have already been removed from the memory.
Popular Posts
Author
-

Naveen Pandey has more than 2 years of experience in data science and machine learning. He is an experienced Machine Learning Engineer with a strong background in data analysis, natural language processing, and machine learning. Holding a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology from Sikkim Manipal University, he excels in leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs), TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face to develop innovative solutions.
View all posts

