Default argument and Ternary operators in Python
 Naveen
Naveen- 0
The objects like list, dict are mutable. A mutable object can change its state or contents, so whenever we use these types of mutable objects as default argument in Python functions, and execute or call the function multiple times it gives unnecessary output for each function call.
The example shown below is to return the list of even numbers, using the mutable list as default argument (even_list = []).
Example:

As you can see, for the first function call, it returns exactly what we expected. On the second and all subsequent function calls, the same list is used in each call.
Now what we can do for avoiding this type of result is, we can set the mutable default argument as None and assign the mutable data within the function using specific condition.
Example:

Ternary operator provides short and concise way to write the conditional statements and allows to evaluate and test the condition in a single line of code.
Syntax:
True_value if condition else false_value
Example:

Like as ternary operator using if..else we can also implement the same using list, tuple, dictionary and lambda.
Using List
Syntax:
[false_value, true_value][condition]

Using Dictionary
Syntax:
{True: true_value, False: false_value} [condition]

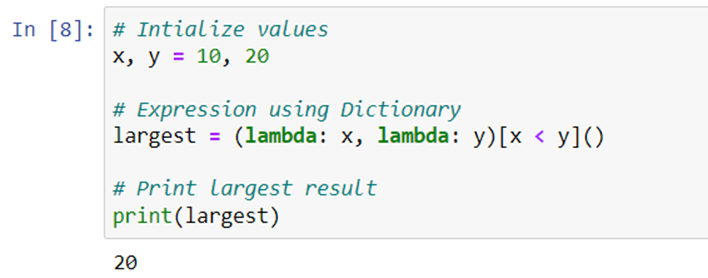
Using Lambda
Syntax:
(lambda: false_value, lambda: true_value) [condition]()
Popular Posts
Author
-

Naveen Pandey has more than 2 years of experience in data science and machine learning. He is an experienced Machine Learning Engineer with a strong background in data analysis, natural language processing, and machine learning. Holding a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology from Sikkim Manipal University, he excels in leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs), TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face to develop innovative solutions.
View all posts

